Client in Java
From Section 7.2 of the book
This example shows how to write a Java client for the
TimeService.
client/javaclient/JavaClient.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
/** A simple web service client in Java.
The web service is invoked via SOAP and HTTP and prints
the result to the console.
*/
public class JavaClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url= new URL("http://dotnet.jku.at/book/samples/7/simple/TimeService.asmx");
// open an HTTP connection to the web service
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");
connection.setDoOutput(true);
connection.setDoInput(true);
// make it a SOAP request
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-type", "text/xml; charset=utf-8");
connection.setRequestProperty("SOAPAction", "http://tempuri.org/GetTime");
// build the SOAP request for GetTime
//http://localhost/time/TimeService.asmx?op=GetTime
String msg =
"<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?>\n" +
"<soap:Envelope " +
//" xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\"\n" +
//" xmlns:xsd=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema\"\n" +
" xmlns:soap=\"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/\">\n" +
" <soap:Body>\n" +
" <GetTime xmlns=\"http://tempuri.org/\" /> \n" +
" </soap:Body>\n" +
"</soap:Envelope>";
// send the SOAP request
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-length", String.valueOf(bytes.length));
// output
System.out.println("\nSOAP call:");
System.out.println("Content-type:"+connection.getRequestProperty("Content-type"));
System.out.println("Content-length:"+connection.getRequestProperty("Content-length"));
System.out.println("SOAPAction:"+connection.getRequestProperty("SOAPAction"));
System.out.println(msg);
OutputStream out = connection.getOutputStream();
out.write(bytes);
out.close();
// read and print the SOAP response
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
connection.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
System.out.println("\nServer response:");
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null)
System.out.println(inputLine);
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("-- error:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
|
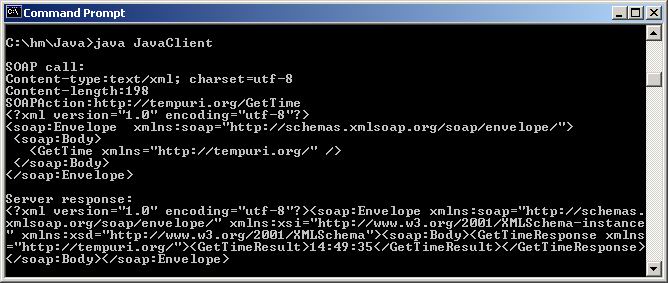
The result is:
|









