|
|
|
Collections
Example "Comparer"
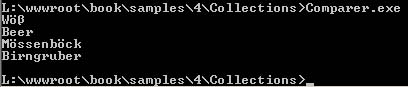
The following example shows the implementation of an IComparer object that performs a string comparison on the basis of length. Note here that a null reference is considered to be the smallest element (in conformance with Microsoft documentation):
/book/samples/4/Collections/Comparer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
public class StringLengthComparer : IComparer {
public int Compare(object x, object y) {
if (x == null && y == null) return 0; // x == y
if (x == null) return -1; // x < y
if (y == null) return 1; // x > y
if (x.ToString().Length == y.ToString().Length) return 0; // x == y
if (x.ToString().Length < y.ToString().Length) return -1; // x < y
return 1; // x > y
}
}
public class TestComparer {
public static void Main() {
string[] a = { "Birngruber", "Woess", "Moessenboeck", "Beer" };
Array.Sort(a, new StringLengthComparer());
foreach (string s in a) Console.WriteLine("{0}", s);
}
}
|
Example "Hashtable"
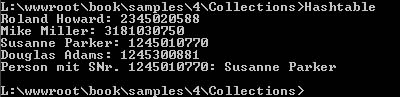
In the following example persons are inserted into a hash table and the social security number is used as key.
/book/samples/4/Collections/Hashtable.cs
public class Person {
string lastName;
string firstName;
public Person(string firstName, string lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName;
}
public override string ToString() {
return firstName + " " + lastName;
}
}
public class HashtableExample {
public static void Main() {
Hashtable tab = new Hashtable();
tab.Add(3181030750, new Person("Mike", "Miller"));
tab.Add(1245010770, new Person("Susanne", "Parker"));
tab.Add(2345020588, new Person("Roland", "Howard"));
tab.Add(1245300881, new Person("Douglas", "Adams"));
foreach (DictionaryEntry e in tab)
Console.WriteLine(e.Value + ": " + e.Key);
if (tab.Contains(1245010770))
Console.WriteLine("Person with SSN 1245010770: " + tab[1245010770]);
}
}
|
|









